Permanent Magnet Variable Frequency Booster Pump
A permanent magnet variable frequency booster pump utilizes permanent magnets and variable frequency drive (VFD) technology to control its operation effectively. Here’s a breakdown of how it works and why it may not require a separate pump controller:
1. Permanent Magnet Motor (PMM):
- Magnetic Field: In a permanent magnet motor, small permanent magnets are attached to the rotor. These magnets create a magnetic field that interacts with the electromagnetic field generated by the stator windings.
- Efficiency: PMMs are typically more efficient than traditional induction motors because they do not draw reactive power and can achieve higher torque density. This leads to better overall performance and energy savings.
- Low Starting Current: Another advantage of PMMs is their ability to start with a lower current than traditional motors, reducing stress on the power supply.
2. Variable Frequency Drive (VFD):
- Speed Control: The VFD adjusts the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for precise control of rotational speed and torque. By varying the frequency, the flow rate can be controlled according to the system's demands.
- Soft Start: VFDs provide a soft start capability, gradually ramping up the motor speed instead of applying full voltage immediately, which reduces mechanical and electrical stress.
- Energy Savings: By adjusting the pump speed to match actual demand rather than running at a constant speed, significant energy savings can be achieved, especially in applications with varying flow requirements.
3. Integrated Control:
- Many modern permanent magnet variable frequency booster pumps have integrated controls that coordinate the motor and VFD functions without the need for a standalone pump controller.
This can include:
- Sensors: Built-in pressure, flow, and temperature sensors that provide real-time feedback to the system.
- Smart Algorithms: Algorithms that optimize pump performance based on input from the sensors, adjusting motor speed and flow rate automatically to match demand.
- User Interfaces: Most pumps come with a user-friendly interface to facilitate setup and monitoring without the complexity of an external control system.
4. Advantages of No Separate Pump Controller:
- Simplicity: This integration reduces the complexity of the system, making it easier to install, operate, and maintain.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminating a separate controller can reduce upfront costs and maintenance requirements.
- Space Saving: Fewer components mean less physical space is needed for installation, which can be a significant advantage in constrained environments.
- Fewer Points of Failure: Having fewer components in the system can also lead to a reduced risk of failure.
Summary
In summary, a permanent magnet variable frequency booster pump operates by employing permanent magnets for efficiency and a VFD for variable speed control. It is designed to function independently, often eliminating the need for a traditional separate pump controller, thanks to integrated controls and sensors that allow for real-time adjustments based on system demands. This results in better efficiency, ease of use, and potentially lower costs and maintenance.
The R Series Permanent Magnet Variable Frequency Booster Pump
This is a small water supply system that boosts household tap water. It's also suitable for supplying water to gardens, hotels, and high buildings.
- pH: 6-8.5
- Ambient Temperature: 0-40 °C
- Medium Temperature: 0-90 °C
- RH: Max.85%
Parameter List
| Model |
Power Supply (V/Hz) |
Suction (m) |
Rated Flow (m3/h) |
Rated Head (m) |
Maximum Flow (m3/h) |
Maximum Head (m) |
Power (W) |
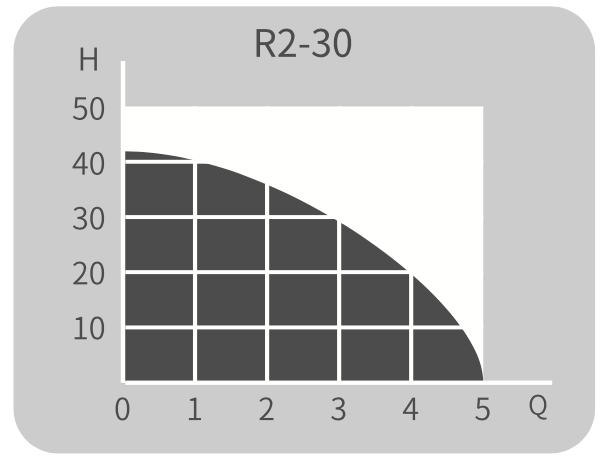
| R2-30 |
220/50 |
8 |
2 |
30 |
5 |
42 |
600 |
Performance Curve
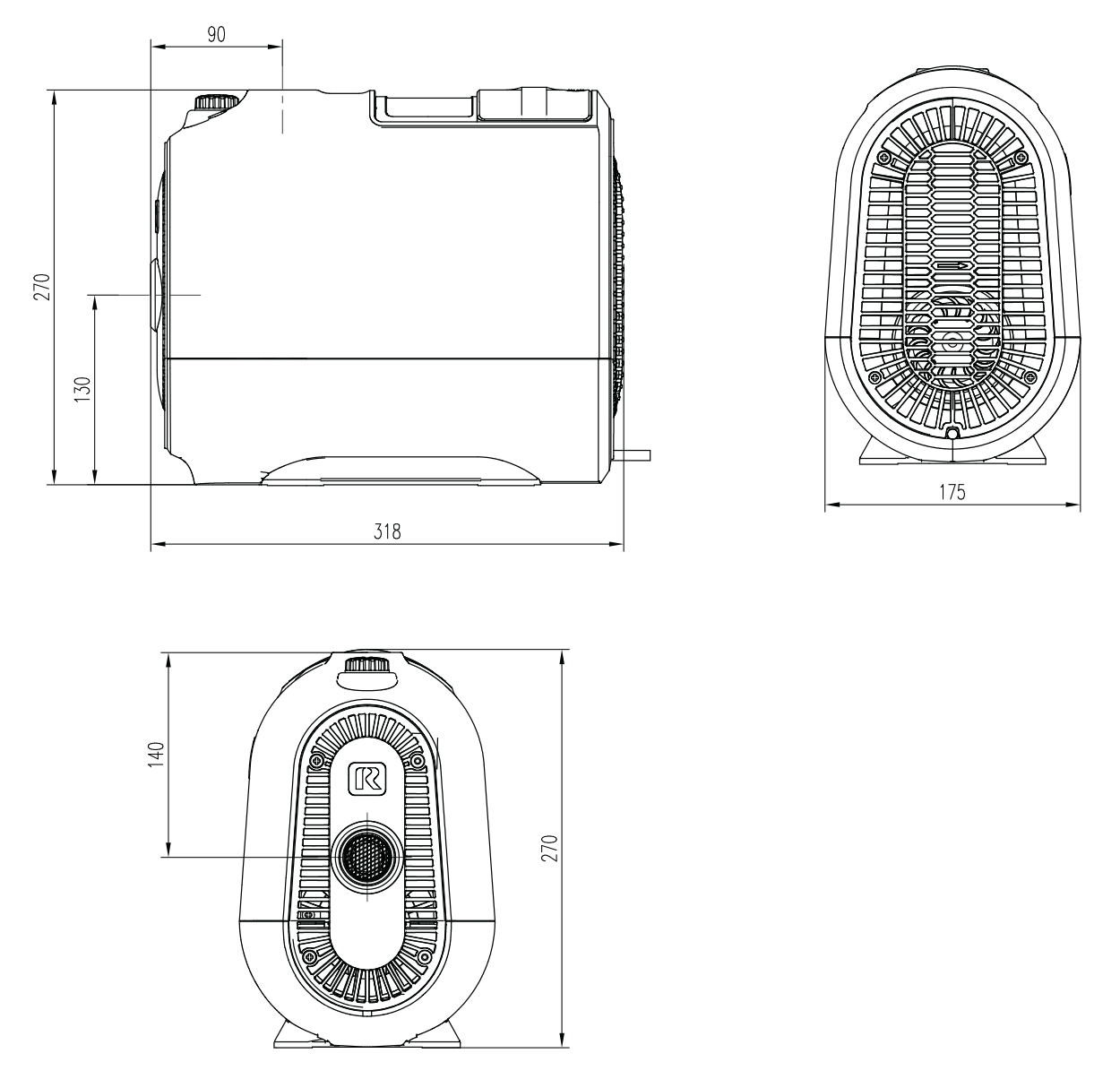
Outline Drawing and Dimensions (mm)
Datasheets
- https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HAInXYfhsGSd-z1a0pCxcvmqYqf7pYxE/view?usp=sharing
- https://drive.google.com/file/d/1LrSMcicuARGT62FoJ5kuualvLj0A1brD/view?usp=sharing




